The U.S. is investing billions of {dollars} to cut back forest hearth dangers. New analysis maps the new spots the place investments in strategic forest administration may provide the most important payoff for folks and local weather.
The Gist
Revealed in Environmental Analysis Letters, the examine, a collaboration amongst The Nature Conservancy, College of Montana and USDA Forest Service, estimated the danger of wildfire-caused carbon loss throughout the conifer forests of the western United States.
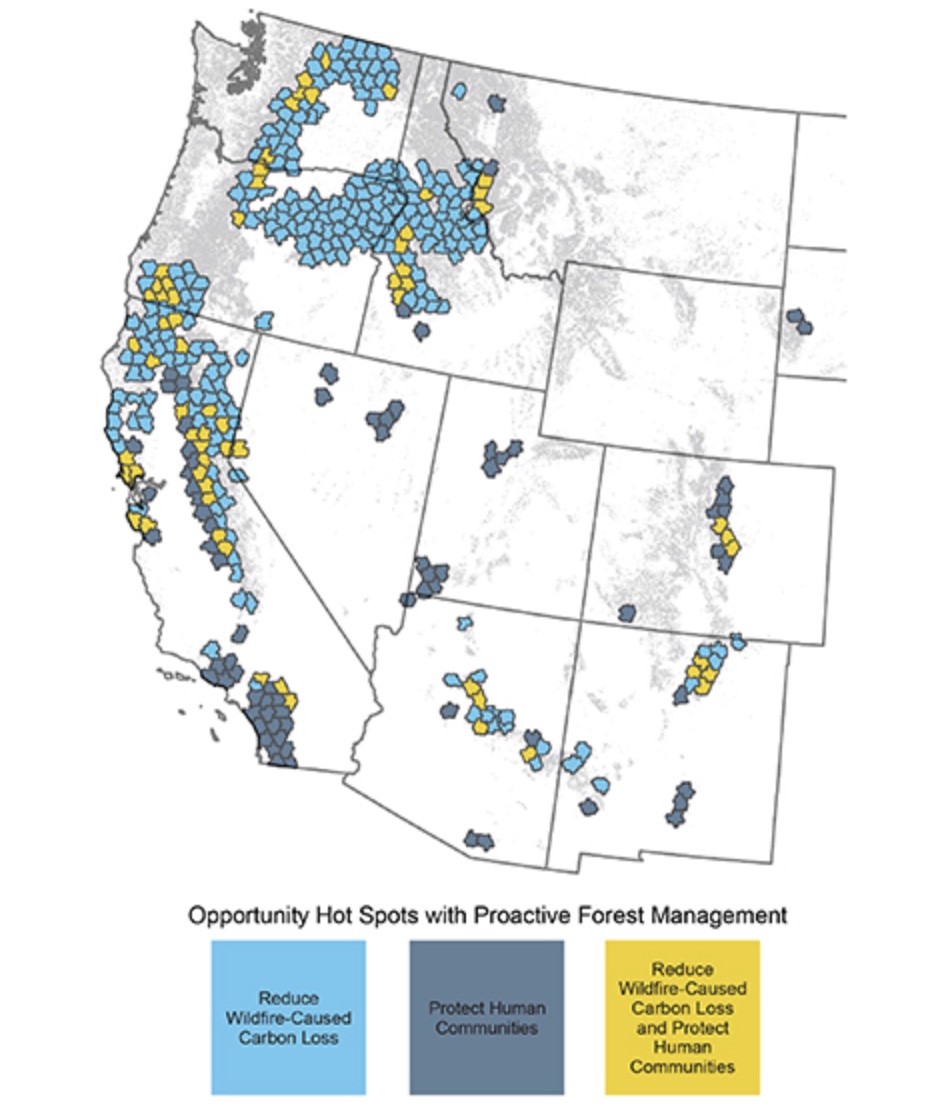
Researchers then in contrast areas recognized as in danger for carbon loss to wildfire to human communities additionally weak to wildfire (as recognized within the Forest Service’s Wildfire Disaster Technique.) The overlap confirmed excessive worth “alternative scorching spots” the place forest administration instruments, corresponding to thinning, prescribed hearth and cultural burning, may scale back danger from wildfire to each carbon storage, and human communities and infrastructure.
The Huge Image
The paper notes that decision-makers don’t essentially want to decide on between climate- and wildfire-mitigation targets. Whereas the examine covers 11 Western states, says co-author, Travis Woolley, forest ecologist for TNC in Arizona. “The necessity for strategic forest administration in California, New Mexico and Arizona is especially pressing, provided that a big portion of their forests are extremely weak to wildfire-caused carbon loss.”
“Our method will help land managers plan the place to put money into proactive forest remedies with essentially the most potential to guard communities,” says lead writer, Jamie Peeler, panorama ecologist and NatureNet Postdoctoral Science Fellow with the College of Montana. “It additionally might be utilized to cut back danger from wildfire to different essential values corresponding to municipal water, culturally essential crops, recreation and wildlife habitats.”
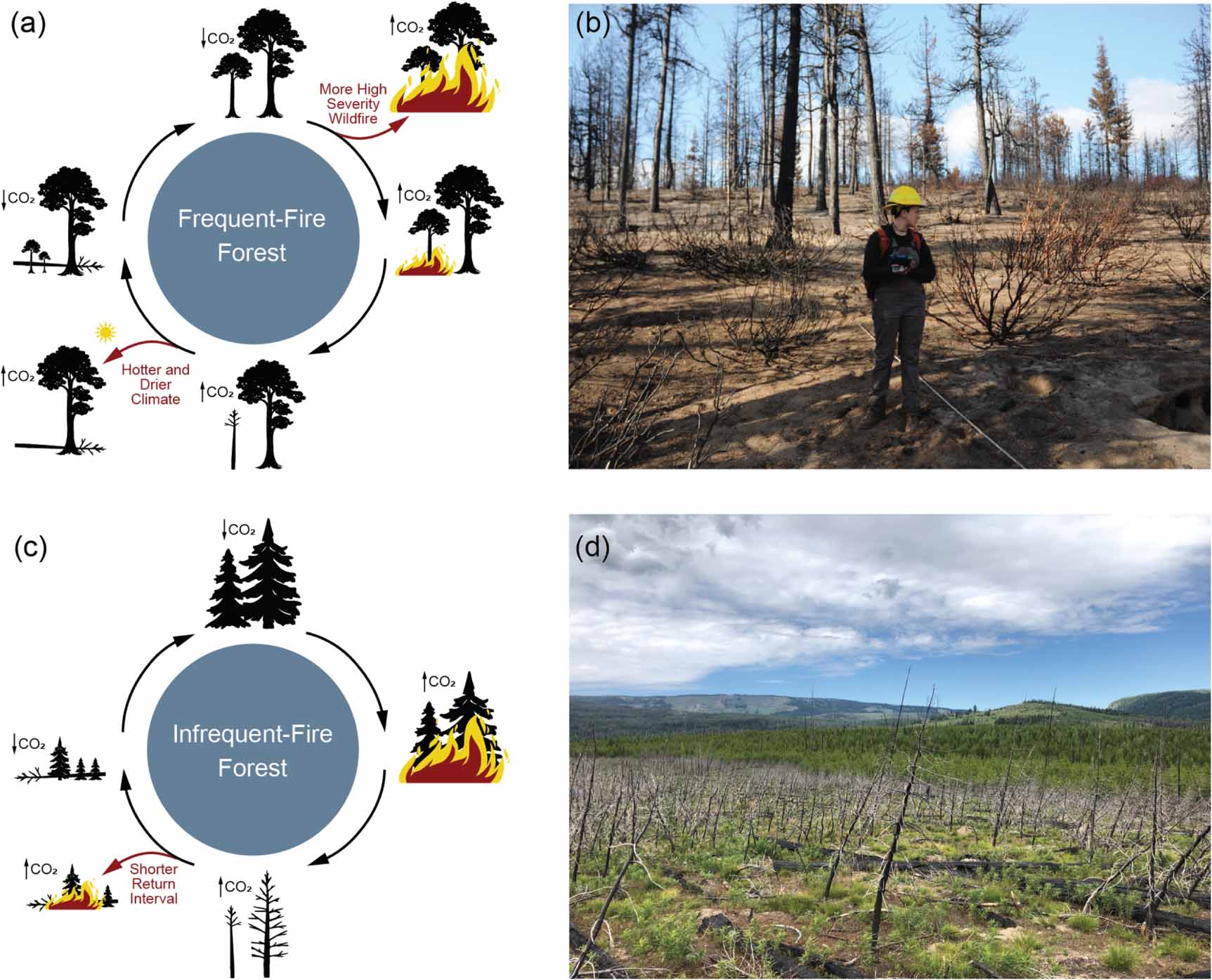
The paper emphasizes that, although “risk-informed prioritization maps can establish goal geographies, they don’t account for complicated social, ecological, political, and financial dynamics occurring domestically.”
The maps, due to this fact, are usually not meant to interchange native knowledges or values that finally inform proactive forest administration. Fairly, they may inform and assist prioritize investments in community-based collaborations that plan, implement, and preserve remedies. Ideally, notice the authors, community-based collaborations symbolize folks and companies that reside in a specific place and share a collective curiosity in its well-being.
The authors additionally spotlight the significance of group involvement in any forest-management planning. And notice particularly it will likely be essential for “community-based collaborations” to prioritize teams with long-standing place-based information, like Tribes, who’ve traditionally been excluded from forest and hearth administration.
The Takeaway
Congress lately handed the Infrastructure Funding and Jobs Act (IIJA) which features a “Wildfire Disaster Technique” to dramatically enhance the tempo of forest restoration throughout the West. The plan consists of unprecedented ranges of funding ($3 billion {dollars}) from the federal authorities to cut back fuels in fire-adapted forests throughout 50 million acres of forests within the subsequent 10 years which is at the very least two instances greater than present charges.
“The sort of science collaboration,” famous USDA Forest Service Chief Randy Moore, “strengthens our efforts to help land managers in designing and implementing efficient tasks with a number of advantages, making good work even higher. It additionally is essential in informing our total efforts to handle the wildfire disaster going through our nation’s forests by doing the precise work, in the precise place, on the proper time.”

